-

Opening Hours
view our working time
-
Call us: +91 4936208777
+919562488777
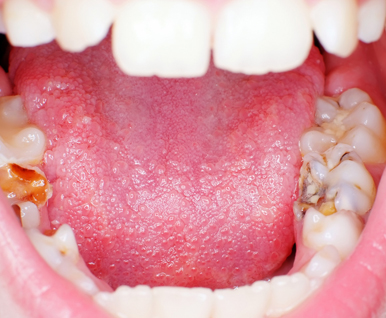
Dental Fluorosis
Dental fluorosis is a known adverse effect of fluoride overuse. Enamel or dental fluorosis is a condition caused by 'excessive' intake of fluoride over an extended period of time. The most common symptom of dental fluorosis is a chalk-like discoloration of teeth with white spots or lines on tooth enamel. In more severe cases the affected areas have a yellow or brown discoloration. In extreme forms, fluorosis may result in a pitted tooth surface.
After the teeth come in, the teeth of those affected by fluorosis may appear mildly discolored. For instance, there may be lacy white markings that only dentists can detect. In more severe cases, however, the teeth may have:
Preventing Dental Fluorosis
Powdered or liquid concentrate infant formula should be mixed with water that is fluoride-free or contains low levels of fluoride, Do not use fluoride toothpaste until the child is two years old unless advised to do so by a dentist,For children age two and older, place only a pea-sized amount of fluoride toothpaste on the toothbrush at eachbrushing, Avoid toothpastes with flavors that may encourage swallowing, An adult should supervise the use of fluoride-containing dental products by children younger than six years old, and check that they do not swallow it.
Treatment
Remember that fluorosis affects only the appearance of teeth. It does not result in cavities. As a result, most of the treatment for fluorosis consists of masking the stain.
Many cases of fluorosis are minor enough not to need treatment. Sometimes fluorosis occurs only on the back teeth, where it can't be seen. More serious cases and cases involving the front teeth can be treated by removing the surface-stained areas throughtooth whitening or other procedures. Severe cases of fluorosis can be covered withbonding, crowns or veneers

